Re: A news item and subject which I just want to check out (142) June 28, 2024
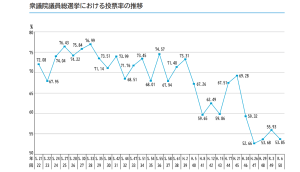
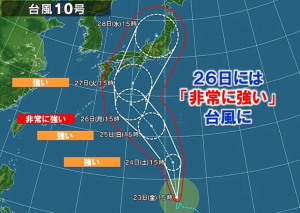
There was an article that the Meteorological Agency is wondering about the announcement of declaration of the start of the rainy season. The rainy season this year certainly varies significantly by region, and there was an announcement that “the rainy season has likely begun” in the Kinki district last week, half a month later than usual. Incidentally, the end of the rainy season is expected to be around mid-July.
On the other hand, in China, record-breaking heavy rain caused severe damage in mid-June, and at least 57 people have been confirmed dead in Guangdong Province and Fujian Province.
And in the United States, record-breaking heat has been observed in various places, and it is said that this year could break the heat in 2023 when record-breaking heat wave occurred. Due to heat wave, floods, wildfires and other impacts are widespread in various places. By the way, in the United States, it is 37 degrees Celsius level of heat wave, but in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the greatest sacred place of Islam an extraordinary heat, 51.8 degrees, was recorded on June 17. Therefore, it is reported that more than 1,300 people died in the middle of the great pilgrimage, Haji.
In the United States, the beginning of the demand for stricter information disclosure from companies by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been gaining attention, because recent abnormal weather can have a significant impact on business performance.
■■What I have recently thought and focused on:
■“Growth vision” that increases “medium-sized enterprises” between small and medium-sized enterprises and large enterprises:
It is pointed out that industrial policy, where it is divided into large enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises by the scale of the capital and the number of employees, is becoming “an obstacle to growth”. In other words, there is a gap in government subsidies and taxation due to differences in scale, and small and medium-sized enterprises don’t dare to aim for growth into large enterprises, in order to receive the benefits. If tracing back, when “Pro Forma Standard Taxation” that collects based on the amount of additional value and capital was introduced as a part of corporate business tax in 2004, delineation of capital between small and medium-sized enterprises and large enterprises was set to 100 million yen. Therefore, the trend of reducing capital to less than 100 million yen has emerged. There was a case that large enterprises that fell into poor performance due to corona disaster reduced the capital to less than 100 million yen and were back to the category of small and medium-sized enterprises and reduced their tax burden. Against a backdrop of such tax system, the number of corporations with “a capital of 100 million yen or more” subject to taxation has been decreasing in Japan. According to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the number in 2021 has decreased by more than 30 % compared to the peak in 2006, and the share of all corporations has also dropped from 1.18 % to 0.72 %. In other words, 99.28 % out of about 3.8 million corporations in Japan are small and medium-sized enterprises with a capital of less than 100 million yen. And this enterprise tier has been targeted by economic measures that the government comes up with every year such as subsidies for promoting digitalization and loan without interest and collateral substantially (zero-zero loan). And a burden of social security costs has also been reduced. It seems to me that such support measures or privilege measures limited to small and medium-sized enterprises foster, so to speak, relying on each other between the government and the industry, and hinder restructuring and elimination, and this is one of the reasons for the multi-layered structures such as main contractor, subcontractor and sub-subcontractor. As a result, it can’t be denied that in Japan, a distorted reality where 60 % of all business operators don’t or can’t pay taxes is formed and low productivity is being caused. I think that as it is, government subsidies are too fragmented and not expected to be effective, and on top of that, enterprises can’t bear the necessary investment for correspondence to the shortage of human resources and labor shortage associated with declining birthrate and aging population, computerization and digitalization towards informatization and research and development.
In consideration of such structural issues in Japan, the government decided to formulate “growth vision” in order to aim for the increase of “medium-sized enterprises” with 2,000 or fewer employees that are positioned between large enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises. It has been pointed out that public support for this tier is scarce compared to small and medium-sized enterprises and large enterprises. Therefore, in Japan, even though becoming medium-sized enterprises from small and medium-sized enterprises, the share that grows from there further to large enterprises is said to remain about 10 %. Incidentally, it is said that in the United States, it is 30 % and 20 % in Europe, I think the difference seems to be partly due to variations in industrial policy. It is necessary to restructure and integrate to a certain size of enterprise, and try to improve efficiency of human resources and fund efficiency, and to contribute to productivity improvement ultimately.
■It is necessary to foster startup, corporate or individual that starts a new business:
In Japan, so called unicorn that is an “unlisted venture company with market capitalization of over 1 billion dollars” is very few. According to the research company in the United States, as of March this year, there are 7 in Japan, 656 in the United States and 168 in China, and there is a big difference.
The government established “five-year plan for fostering startup” in 2022, and positioned open innovation (moving away from self-sufficiency) that encourages collaboration with large enterprises on the pillar. And if individual investor invests startup, policy like “angel tax system” that receives tax benefits is also taken.
By the way, in Japan, there are many smaller-sized enterprises working on decarbonization that is a global issue, artificial intelligence (AI), semiconductor, fuel cell, medical and so on, but they don’t grow to be unicorns. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry believes that an old practice like “small and medium-sized enterprises do business as subcontractors supporting specific large enterprises” is also involved here, and it tends to be an unfavorable contract, and formulates standard contract reviewing it and promotes its use.
In Japan, even now, there ae customs that are like remnants of the feudal era such as up and down consciousness like “main contractor and subcontractor” and calling supplier as “donor”, the giver of grace, in the construction industry. This is one of “common sense in Japan is nonsense elsewhere” that there are many. But I think that old trading practices will be forced to change from now on, because the flow of information will change from “vertical type” to “simultaneous and horizontal type” due to spread of IT and DX.
■The movement toward reorganization in the logistics industry:
Due to labor shortage and regulations on working hours called “2024 issue”, even in the logistics industry, M&A that is business acquisitions and reorganization, cooperative delivery in different industries or the same industry, larger vehicles and other movements are finally in full swing. Among them, M&A is one of important corporate strategies now, and I feel the atmosphere of “not being behind the flow”. But it is also true that there are many examples of failures. Key points of M&A are “fully identifying the synergistic effect” and PMI (Post Merger Integration), in other words, “how do you get your business operations on track after integration?”. With money, you can buy things and companies. But putting the blood into it and inserting the soul is done by human resources. It is necessary to identify management resources (people, goods and money) you have, and think deeply about the meaning and purpose of M&A, and create a system for success. I think I will discuss it at another time.